Acl
20 Excel Age Calculations: Ultimate Dd Mm Yyyy Tutorial

Introduction to Excel Age Calculations
Excel is a powerful tool used for various calculations, including age calculations. Calculating age in Excel can be useful in various scenarios, such as tracking employee ages, calculating retirement eligibility, or determining age-based benefits. In this tutorial, we will explore 20 Excel age calculations that can help you master the art of calculating ages in Excel.
Understanding Date Formats

Before diving into age calculations, it’s essential to understand the different date formats used in Excel. The most common date format is DD MM YYYY, which represents the day, month, and year. Excel also recognizes other date formats, such as MM DD YYYY and YYYY MM DD. It’s crucial to ensure that your date formats are consistent throughout your spreadsheet to avoid errors in age calculations.
Basic Age Calculations

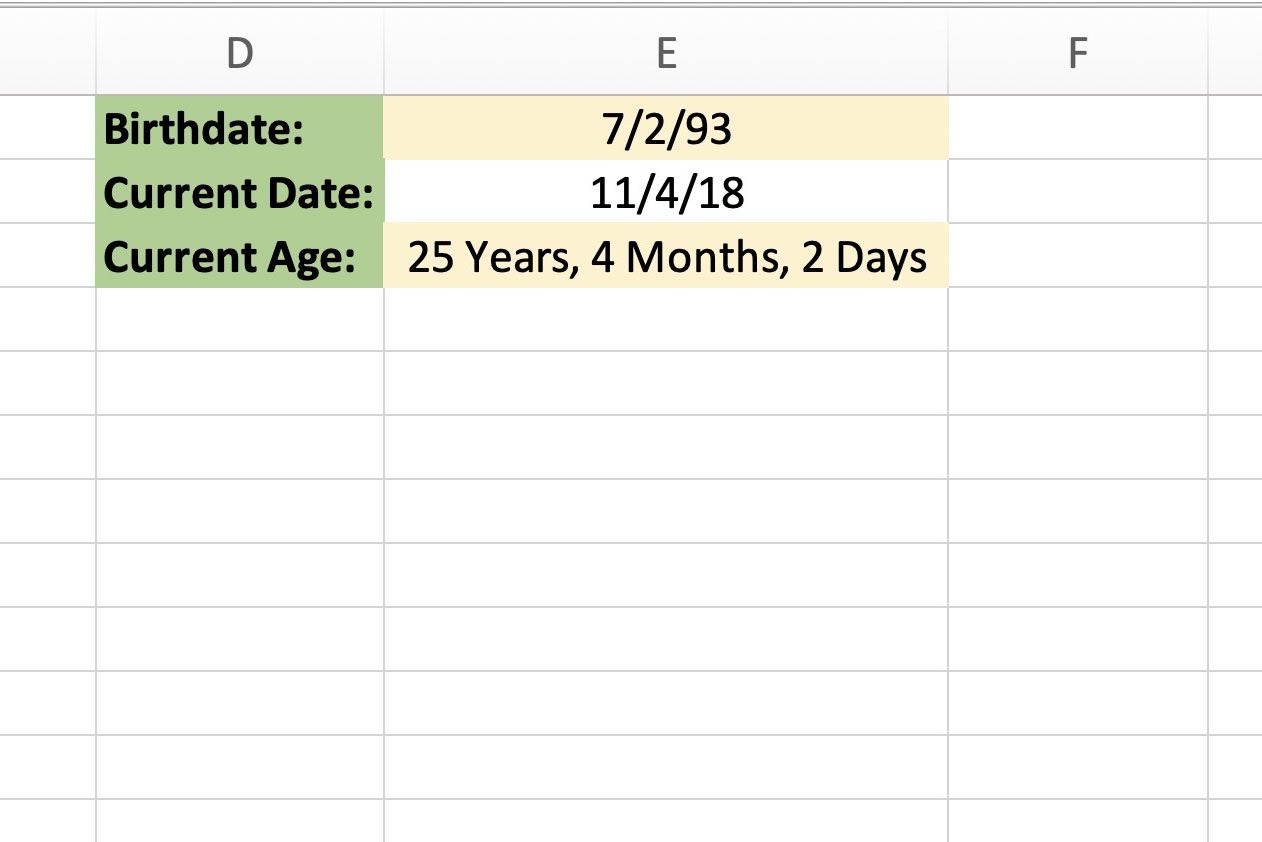
To calculate age in Excel, you can use the DATEDIF function, which calculates the difference between two dates in a specified interval, such as days, months, or years. Here’s an example of how to use the DATEDIF function:
| Birth Date | Current Date | Age |
|---|---|---|
| 01/01/1990 | 01/01/2022 | =DATEDIF(A2,B2,“Y”) |

In this example, the DATEDIF function calculates the age in years between the birth date (01/01/1990) and the current date (01/01/2022).
Advanced Age Calculations

In addition to basic age calculations, Excel offers more advanced functions, such as the TODAY function, which returns the current date, and the EDATE function, which calculates a date a specified number of months before or after a given date. Here are a few examples of advanced age calculations: * Calculating age in months: =DATEDIF(A2,TODAY(),“M”) * Calculating age in days: =DATEDIF(A2,TODAY(),“D”) * Calculating retirement age: =EDATE(A2,65*12)
📝 Note: When using the DATEDIF function, ensure that the birth date is in cell A2 and the current date is in cell B2.
Age Calculations with Multiple Conditions

In some cases, you may need to calculate age based on multiple conditions, such as calculating age for employees who are eligible for retirement. To achieve this, you can use the IF function in combination with the DATEDIF function. Here’s an example: =IF(DATEDIF(A2,TODAY(),“Y”)>=65,“Retired”,“Not Retired”)
Common Age Calculation Errors

When calculating age in Excel, it’s common to encounter errors, such as incorrect date formats or invalid dates. To avoid these errors, ensure that your date formats are consistent and that you’re using the correct functions for your calculations. Here are some common age calculation errors to watch out for: * Incorrect date formats: Ensure that your date formats are consistent throughout your spreadsheet. * Invalid dates: Check that your dates are valid and not incorrect or fictional.
📝 Note: When troubleshooting age calculation errors, check your date formats and functions to ensure they're correct.
Best Practices for Age Calculations

To ensure accurate age calculations, follow these best practices: * Use consistent date formats throughout your spreadsheet. * Use the correct functions for your calculations, such as the DATEDIF function for calculating age. * Double-check your dates to ensure they’re valid and correct. * Use the TODAY function to ensure your calculations are up-to-date.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts

In this tutorial, we’ve explored 20 Excel age calculations that can help you master the art of calculating ages in Excel. By following the best practices outlined in this tutorial and using the correct functions for your calculations, you can ensure accurate age calculations and avoid common errors. Remember to always double-check your dates and use consistent date formats throughout your spreadsheet.
What is the most common date format used in Excel?

+
The most common date format used in Excel is DD MM YYYY, which represents the day, month, and year.
How do I calculate age in Excel using the DATEDIF function?

+
To calculate age in Excel using the DATEDIF function, use the following formula: =DATEDIF(A2,B2,“Y”), where A2 is the birth date and B2 is the current date.
What are some common age calculation errors to watch out for?

+
Common age calculation errors to watch out for include incorrect date formats, invalid dates, and using the wrong functions for your calculations.



