15 Excel Formulas: Ultimate Years Of Service Calculator Guide
Unlocking the Power of Excel: Mastering the Years of Service Calculator

Microsoft Excel is a powerful tool used by millions of people around the world for various purposes, including data analysis, budgeting, and calculations. One of the most useful applications of Excel is creating a years of service calculator, which can be used to track employee tenure, calculate benefits, and make informed decisions. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the 15 Excel formulas that will take your years of service calculator to the next level.
Before we dive into the formulas, it’s essential to understand the importance of having an accurate and efficient years of service calculator. Calculating years of service can be a complex task, especially when dealing with large datasets or intricate payroll systems. By mastering these 15 Excel formulas, you’ll be able to simplify the process, reduce errors, and make data-driven decisions with confidence.
Understanding the Basics: Date and Time Functions
To create a years of service calculator, you need to understand how to work with dates and times in Excel. The following formulas are essential for calculating years of service:
- TODAY(): Returns the current date
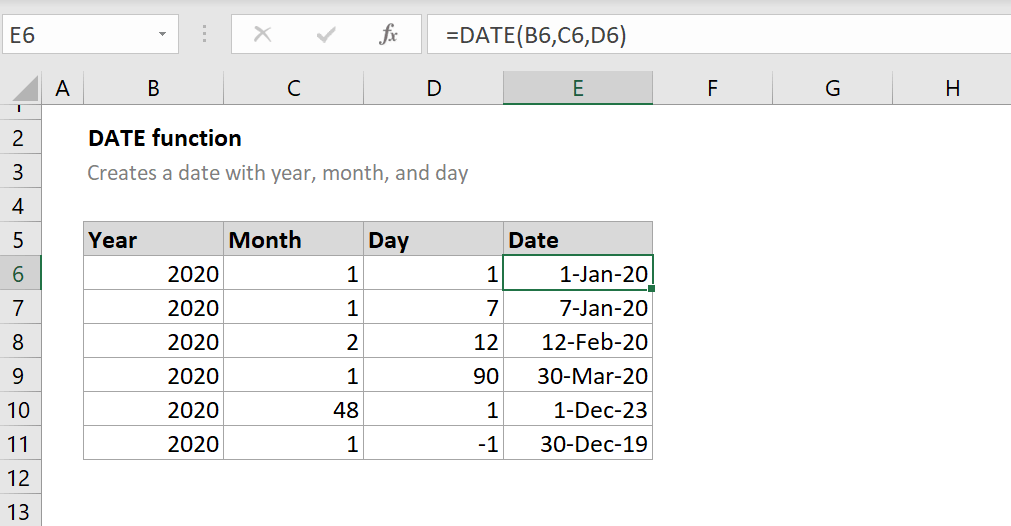
- DATE(year, month, day): Returns a date based on the input year, month, and day
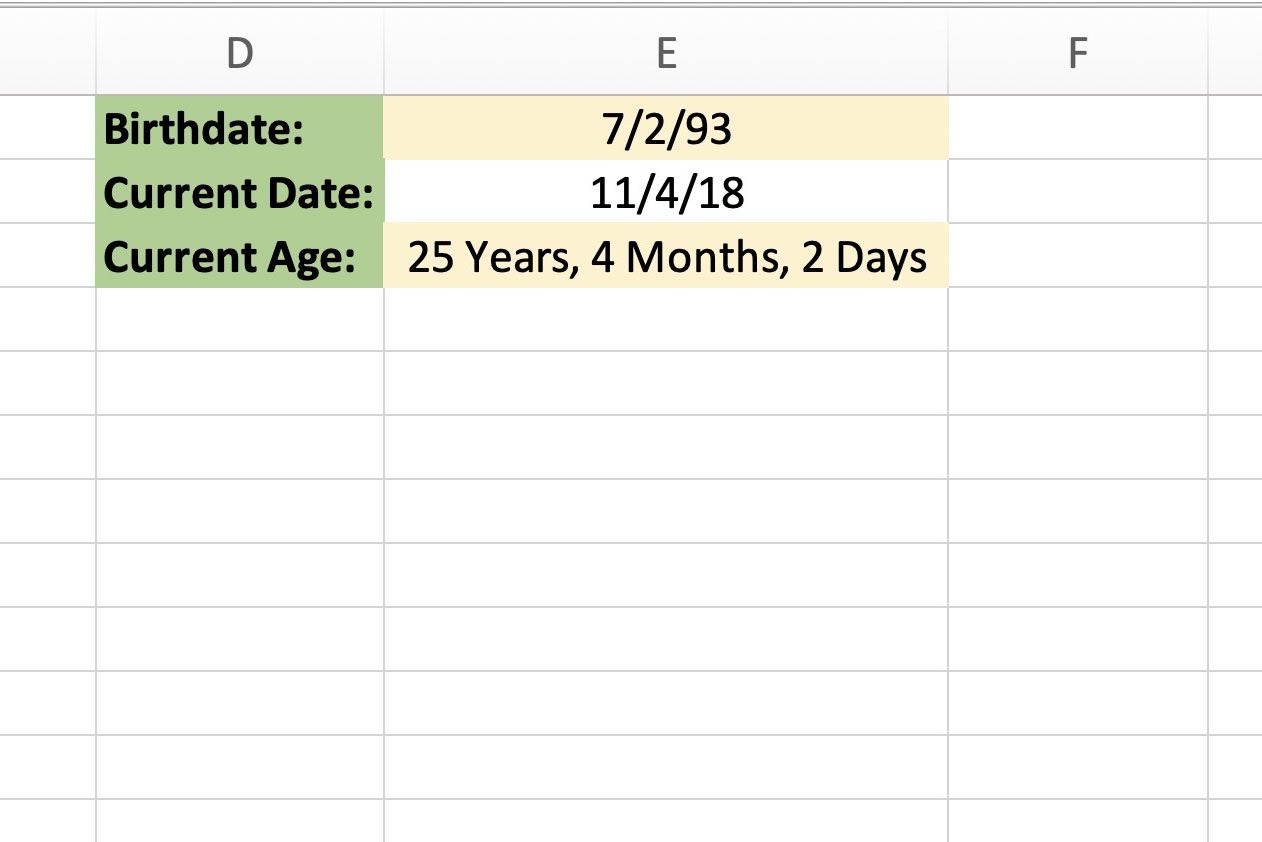
- DATEDIF(start_date, end_date, unit): Calculates the difference between two dates in a specified unit (e.g., days, months, years)
These formulas will help you calculate the current date, an employee’s hire date, and the difference between the two dates.
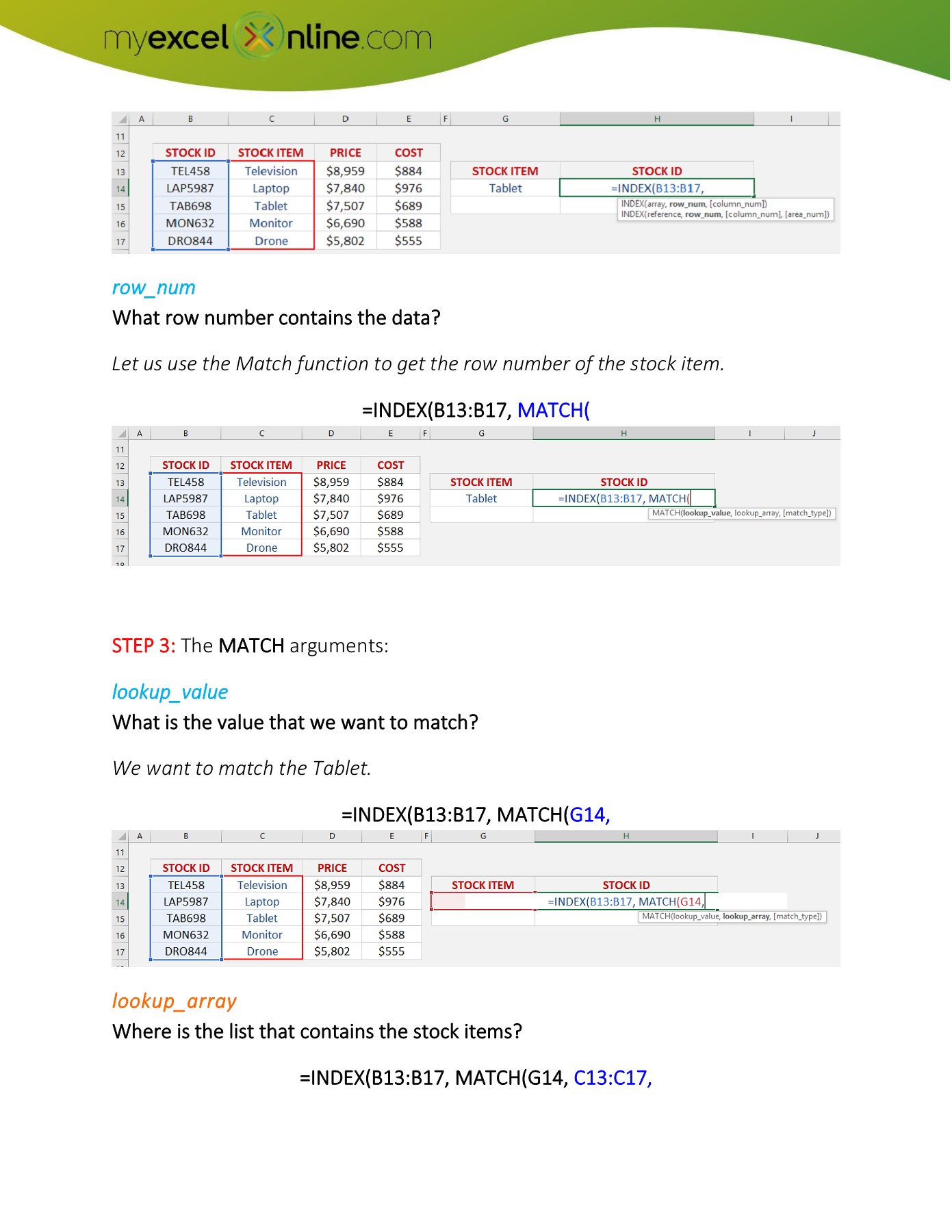
Calculating Years of Service: Advanced Formulas
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s move on to the advanced formulas that will help you calculate years of service:
| Formula | Description |
|---|---|
| =DATEDIF(A2, TODAY(), “y”) | Calculates the number of years between the hire date (A2) and the current date |
| =DATEDIF(A2, TODAY(), “ym”) | Calculates the number of months between the hire date (A2) and the current date |
| =DATEDIF(A2, TODAY(), “yd”) | Calculates the number of days between the hire date (A2) and the current date |
These formulas will help you calculate the years of service in years, months, and days.
Conditional Statements and Formatting
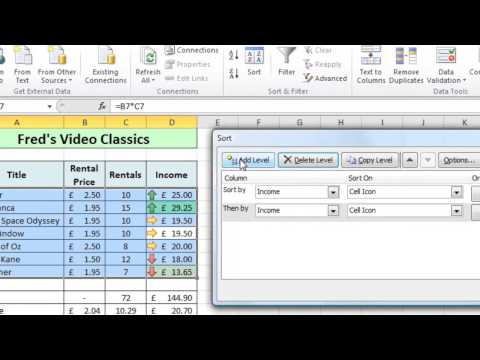
To make your years of service calculator more interactive and user-friendly, you can use conditional statements and formatting:
- IF statement: Used to evaluate a condition and return a value based on the result
- Conditional formatting: Used to highlight cells based on specific conditions (e.g., years of service greater than 5)
These formulas will help you create a more dynamic and engaging years of service calculator.
Mastering the 15 Excel Formulas
Here are the remaining 15 Excel formulas that will help you take your years of service calculator to the next level:
- =EOMONTH(A2, 0): Returns the last day of the month based on the hire date (A2)
- =EOMONTH(A2, -1): Returns the last day of the previous month based on the hire date (A2)
- =NETWORKDAYS(A2, TODAY()): Calculates the number of workdays between the hire date (A2) and the current date
- =WORKDAY(A2, 365): Calculates the date 365 days after the hire date (A2), excluding weekends and holidays
- =ISOWEEKNUM(A2): Returns the ISO week number based on the hire date (A2)
- =WEEKNUM(A2): Returns the week number based on the hire date (A2)
- =MONTH(A2): Returns the month based on the hire date (A2)
- =DAY(A2): Returns the day based on the hire date (A2)
- =YEAR(A2): Returns the year based on the hire date (A2)
- =DATEDIF(A2, TODAY(), “y”) & “ years”: Returns the years of service with the label “years”
- =DATEDIF(A2, TODAY(), “ym”) & “ months”: Returns the months of service with the label “months”
- =DATEDIF(A2, TODAY(), “yd”) & “ days”: Returns the days of service with the label “days”
These formulas will help you create a comprehensive and accurate years of service calculator.
📝 Note: Make sure to adjust the formulas to fit your specific needs and data structure.
In summary, mastering the 15 Excel formulas outlined in this guide will help you create a powerful and efficient years of service calculator. By combining these formulas with conditional statements and formatting, you'll be able to track employee tenure, calculate benefits, and make informed decisions with confidence.
What is the purpose of a years of service calculator?
+
A years of service calculator is used to track employee tenure, calculate benefits, and make informed decisions.
What are the basic date and time functions in Excel?
+
The basic date and time functions in Excel include TODAY(), DATE(), and DATEDIF().
How do I calculate years of service using Excel formulas?
+
You can calculate years of service using formulas such as =DATEDIF(A2, TODAY(), “y”), =DATEDIF(A2, TODAY(), “ym”), and =DATEDIF(A2, TODAY(), “yd”).



